Digital Badges: why they are important for engagement?
Originally badges were a heraldic symbol worn by knights, which were later worn as jewelry, or to denote the completion of a pilgrimage or as a mark of political allegiance. In rituals the badge has long been associated with displays of rank and achievement, and more recently has been associated with advertising, branding and visual identification[1].
Digital badges seem to be a metaphorical and more flexible extension of recognition practices such as the merit badges used by the Boy Scouts association around the globe. The merit badges demonstrated at an established standard or level of practice, a model that suits the educational context especially well.
In our culture there are many ways to recognize an achievement, and many forms of proof for a variety of needs.
« A Digital Badge serves both as recognition of learning or achievement and digital proof of that accomplishment. »
For example, those who walk 10,000 steps are celebrated with the “sneakers” digital badge from their Fitbit, while those who achieve a step count of 100,000 or more are adorned a much more rare, “Olympian Sandals” badge.
« Broadly speaking, a digital badge is an indicator of accomplishment or skill acquired that can be shared, accessed, and verified online »
Specifically, digital badges are a precise case of digital credentials.
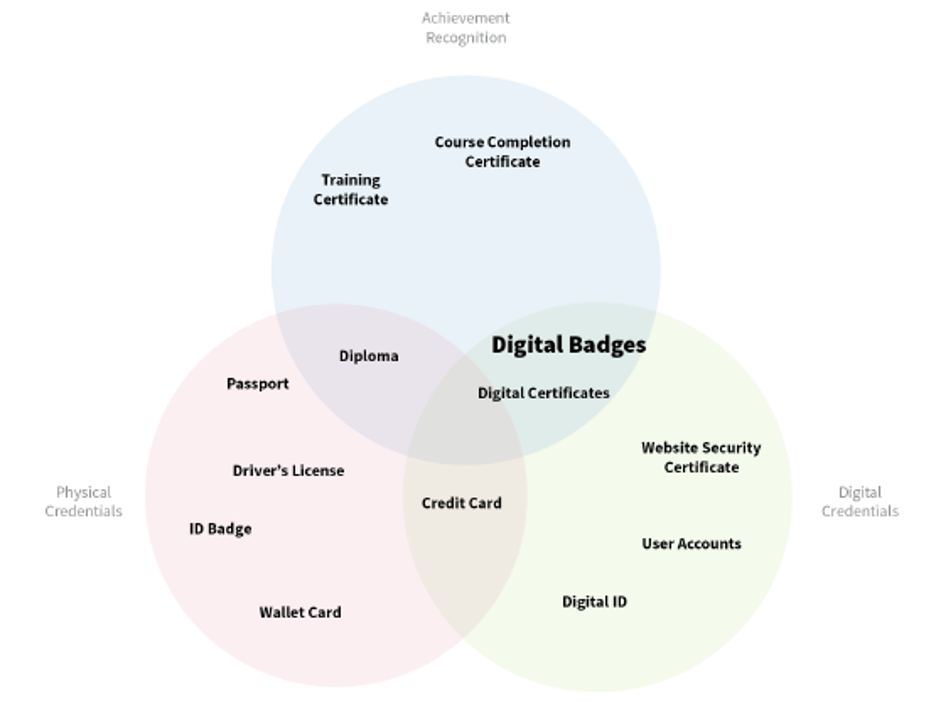
Digital Badges Framework[2]

Historically, the idea of digital badges appeared for the first time in 2011 when Peer 2 Peer University and The Mozilla Foundation published a paper titled “An Open Badge System Framework.” In this paper, a badge was defined as “a symbol or indicator of an accomplishment, skill, quality or interest”.
The paper explained how the context is more important than design: “the information linked to or ‘behind’ each badge serves as justification and even validation of the badge”.
In 2012, the Mozilla Foundation developed an open technical standard called Open Badges which aimed at being the standard for issuing, collecting, and displaying digital badges. Today Open Badges is the world’s leading format for digital badges. Open Badges is not a specific product or platform, but a type of digital badge that is verifiable, portable, and packed with information about skills and achievements[3].

According to the Open Badge standards, for a digital badge to be Open Badge compliant, it needs to have certain required meta-data:
- Badge Name
- Badge Criteria (Often written in the description section)
- Badge URL
- Issue Date
- Issuer (an account or record associated with the organization issuing the badge –
at least their name) - Recipient (an email or user account associated with the badge owner)
In other words, metadata embedded into an open badge have to be able to tell anyone: who received the badge, who issued the badge, what was the criteria for issuing the badge and if there is an expiration date.
So, today, why are Open Badges so important for organizations and HR managers? In Human resources and specifically in Digital Transformation projects, what can badges be used for? Let’s see some applications…
Talent mapping at the nano level to support reskilling and upskilling
Badges allow any organization to create heat maps of the talent and skills really developed by employees. In most educational programs, traditional assessments provide a single quantitative grade. Even if competences can be acquired with a long training on multiple topics, more often than not, some kind of “pass – fail” scale is used to measure and certify the new competence acquired.
Badges provide a more modular, precise and flexible way of showing various levels. Data can be used to assess and track the competences accumulated by employees during formal trainings or with informal activities. The map can then be used to analyse the possible gap between skills distributed in the company or those which are missing. Upskilling or reskilling projects can then be better managed and focused.
For social and organisational recognition
Brands are today one of the strongest social recognition opportunities: wearing a luxury brand or driving a prestigious car is something that creates social and personal recognition.
In a similar way, digital badges can be shown and shared easily and can be a source of pride and belonging to a team with specific and valuable skills.
Employees can be motivated to be part of change programs or trainings or to adopt a new software by leveraging the social component of the digital badges.
Motivate Participation
Employees can become billboards by sharing new badges on LinkedIn, Facebook or Twitter feeds, as well as in their email signatures.
For example the IBM Open Badge program[4] revealed how open badges can convert to real value for an organisation. Within a few months of the program’s launch, IBM obtained some very interesting results:
- 125% increase in new participants
- 226% increase in course completion rates
- 694% increase in course exam pass rates
- 64% increase in product trial downloads.
Personal branding for badge earners
As already stated, as an industry standard with a structured portfolio or backpack to store badges, open badges allow badge earners to share achievements and skills with hundreds or thousands of people with the click of a button. Among other values, this opportunity makes personal branding easier and real for a large number of employees.
Viral marketing for organizations issuers
When employees share online badges not only are they broadcasting details of their skills, but they are also communicating about the issuer’s (i.e. employer’s) brand. IBM generates about 2.5 million social media impressions for every 10,000 badges, saving hundreds of thousands of dollars of viral social media marketing.
Broadly speaking digital badges today represent a huge opportunity for any organization looking to create value for and with its own employees.
Digital badges constitute a technological solution, able to add value to a traditional and consolidated habit. That’s why they are a scalable and fast to implement, although they need to be carefully planned and well implanted into a global HR strategy.
Once deployed they transfer immediate value to employees and employers.
[1] J. M. Spector, The SAGE Encyclopedia of Educational Technology (2015)
[2] Accredible.com, “A comprehensive guide to digital badges” (2017)
[3] “Open Babges” https://openbadges.org (accessed Jan. 20, 2021)
[4] “IBM Credentials” https://www.ibm.com/training/credentials (accessed Jan. 20, 2021)
WANT TO RECEIVE OUR LATEST THOUGHT LEADERSHIP CONTENT?
Related posts
 Take the Guesswork out of People Management
Take the Guesswork out of People Management
 From processes to people: achieving quality
From processes to people: achieving quality
 Daring to lead Positive Transformation: What if Positive Emotional Capital was your key to sustainable change?
Daring to lead Positive Transformation: What if Positive Emotional Capital was your key to sustainable change?
 Why hire Change management professionals? We can do it alone!
Why hire Change management professionals? We can do it alone!
 Digital Transformation and Change Management: Lessons shared in an event hosted by Cebi and MindForest
Digital Transformation and Change Management: Lessons shared in an event hosted by Cebi and MindForest



